News
New Type of Qubit with Tunable Speed and Frequency
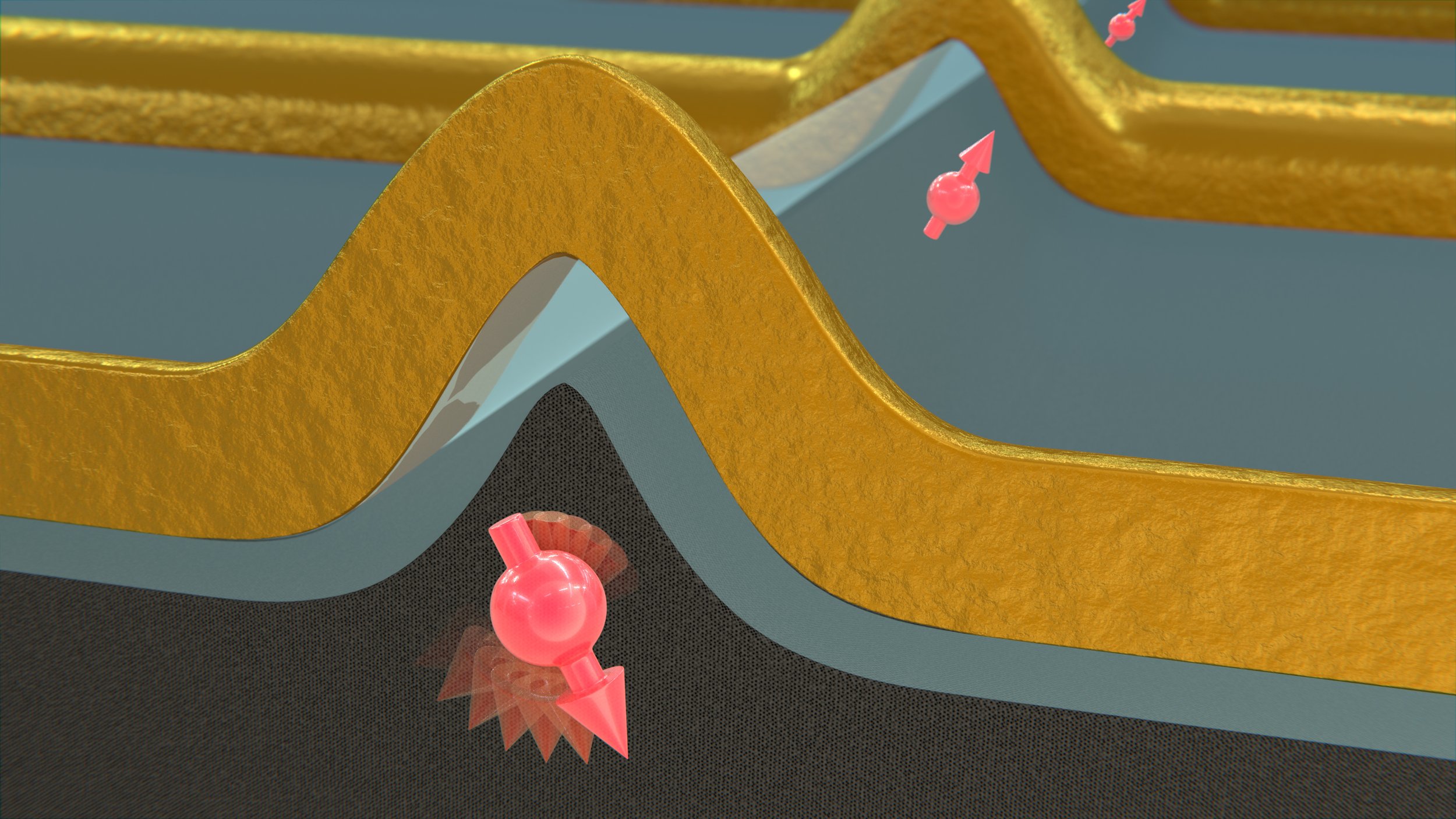
Physicists from the University of Basel and the TU Eindhoven have demonstrated a new type of qubit – the basic building block of a quantum computer – where the speed and frequency of operation can be widely tuned with a gate voltage. They used this flexibility to optimize the hole spin qubit to operate very fast, coherently flipping the spin from up to down in as little as ~1 ns – approaching the clock speeds of today’s computers. The experiment is a big step towards interconnecting and scaling to larger numbers of qubits and thus towards the ultimate goal of building a quantum computer.
Loss-DiVincenzo Proposal listed as Milestone Paper
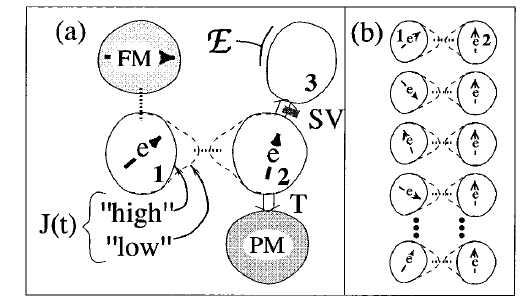
More than 20 years ago, Daniel Loss and David DiVincenzo proposed an electrically controllable quantum computer based on quantum dots. Their paper is listed among Physical Review A's 50th Anniversary Milestones.
Silicon Spin Qubits for Large-Scale Quantum Computing EU Quantum Flagship Program
Another great success for Basel Quantum Physics: Dominik Zumbühl and Daniel Loss have won a new Quantum Flagship project together with a consortium of 10 partners from 8 European countries. The project “QLSI” - Quantum Large Scale Integration in Silicon is funded with 15 million Euros and will run for four years.
NCCR SPIN Announced
The Swiss National Science Foundation and the Federal Government announced that “SPIN: Spin Qubits in Silicon” is one of six newly launched National Centers of Competence in Research.